As we close the chapter in 2024, conflicts continue to rage across various regions worldwide. Despite ongoing efforts aimed at establishing peace, hostilities remain intense on multiple fronts, heightening the risk of a broader global confrontation.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi repeatedly reiterated the country’s commitment to the principle of “no era of war,” urging global leaders to embrace “Peace, Dialogue, and Diplomacy.” However, India also recognised the necessity of bolstering its defence capabilities to assert itself as a recognised regional power.
In addition, increasing disturbances in neighbouring regions amplified India’s imperative to enhance its defence strategy to safeguard its national interests.
In response, India has made significant enhancements to its military arsenal in 2024 to address its security requirements.
Notably, these advancements not only strengthened the nation’s military capabilities but also advanced the ambitious Make in India initiative.
Most of these enhancements were either fully domestically produced or comprised of substantial components manufactured within India.
Following are the latest additions to the Indian armed forces:-
AK-203 rifles

The AK-203 is a modernised version of the renowned Kalashnikov series, chambered for the 7.62×39mm cartridge. In 2024, the Indo-Russian joint venture, Indo-Russia Rifles Private Limited (IRRPL), delivered 35,000 AK-203 rifles to the Indian Army, enhancing infantry capabilities with improved accuracy, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
ASMI SMGs

The ASMI is an indigenous 9mm submachine gun developed by the Indian Army’s Infantry School and DRDO. Designed for close-quarter battles, it offers a compact and lightweight solution for counter-terrorism and special operations. In 2024, the Indian Army inducted 550 ASMI units into the Northern Command, bolstering its close-combat arsenal.
BHISHM Cubes
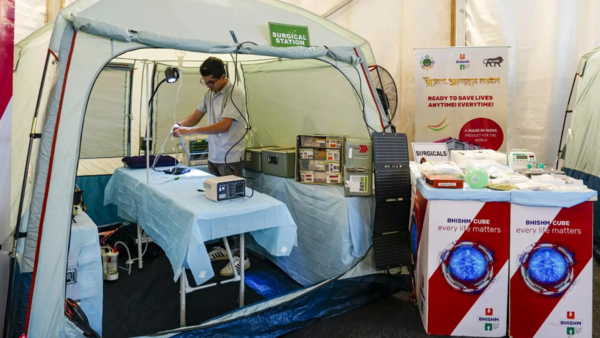
BHISHM Cubes are innovative mobile medical units developed under Project BHISHM (Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita and Maitri). They are designed to provide emergency medical care, particularly in conflict zones and disaster-affected areas. Equipped with trauma, burn, and surgical facilities, they operate autonomously with power and oxygen generation.
Agniastra

It is a portable multi-target detonation device developed by the Indian Army’s Corps of Engineers. This microprocessor-based innovation enhances the safety and efficiency of demolition operations, offering improved range and selective targeting. With a range of 2.5 km, Agniastra proves invaluable in conventional and counter-terrorism operations, such as room interventions, IED destruction and remote bunker or hideout destruction.
Nagastra-1

It is Indian Army’s first indigenous loiter munition, aka suicide drone. A man-portable, electric UAV weighing 9 kg, it features a range of up to 30 km. Equipped with a 1 kg warhead, it offers GPS-enabled precision strikes and a low acoustic signature, making it effective in both day and night operations. It has over 75% indigenous content and its unique recovery and reuse capabilities set it apart from global counterparts.
T-90 Mk-III tanks

India’s defence sector marked a milestone with the rollout of 10 T-90 Mk-III tanks (upgraded version of T-90 Bhishma tanks) by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited. Built at HVF, these tanks feature upgrades like an automatic target tracking system, a digital ballistic computer, and an indigenously developed commander sight. The full batch of 464 tanks will be delivered over five years.
Igla-S MANPADS

In 2024, the Indian Army inducted 24 Russia-made Igla-S MANPADS with 100 missiles to enhance its Very Short Range Air Defence (VSHORAD). This system targets low-flying aircraft, drones, and missiles. The deal includes domestic production through Transfer of Technology, replacing outdated Igla-1M systems.
Akashteer

In 2024, the Indian Army introduced Akashteer, an advanced air defence system. It combines sensors from different sources to create a clear view of the sky, helping the army respond quickly to threats like aircraft and missiles. With over 100 systems delivered, the project will be fully deployed by 2027, strengthening India’s defence.
Sirin Hexadrone

The Indian Army introduced the Sirin Hexadrone, an advanced hexacopter drone designed for combat operations. With a 45-minute flight endurance, it can carry up to 1 kg of armament, including machine guns and grenades. Developed by Ikran Aerospace, it features advanced targeting, encrypted communication, and efficient electric propulsion, enhancing surveillance and reducing soldier fatalities.
INS Tushil

The Indian Navy commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth-guided missile frigate, marking a key milestone in enhancing India’s maritime capabilities. The seventh ship in the Project 1135.6 series, INS Tushil features advanced weaponry like BrahMos missiles and Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles. It integrates 26% indigenous systems.
INS Sandhayak

The Indian Navy commissioned INS Sandhayak, an advanced survey vessel, in Visakhapatnam in 2024. This 110-meter vessel is equipped with cutting-edge sonar systems, enhancing the Navy’s hydrographic survey and ocean research capabilities. With a speed of 18 knots, INS Sandhayak will bolster India’s maritime security and research.
INS Triput

INS Triput is the first indigenously-built Talwar-class frigate of India and was launched in 2024. It was built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL). Part of India’s effort to strengthen its maritime defence, this 124.8-meter ship features advanced stealth technology and powerful weapon systems, including BrahMos missiles.
INS Arighat

India commissioned INS Arighat in 2024, its second nuclear-powered submarine, enhancing its strategic deterrence. Armed with K-15 (750 km range) and K-4 (3,500 km range) submarine-launched ballistic missiles, it joins INS Arihant in strengthening India’s nuclear triad. Powered by a pressurized light-water reactor, INS Arighat ensures survivability for retaliatory strikes, supporting India’s “no-first use” policy.
INS Nirdeshak

INS Nirdeshak, the second ship of the Survey Vessel (Large) project, was commissioned into the Indian Navy in 2024. Built with over 80% indigenous content, it features advanced hydrographic systems for ocean mapping and navigation. The ship supports India’s maritime diplomacy and security in the Indian Ocean Region.
INS Malpe and INS Mulki

Indian Navy launched Malpe and Mulki in 2024, the fourth and fifth ships of the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC) project, which are built by Cochin Shipyard Ltd. The ships, part of the Mahe class, feature over 80% indigenous content and are designed for coastal anti-submarine operations, with speeds of 25 knots and endurance up to 1800 nautical miles.
Drishti 10 starliner drone

India’s Navy acquired its first indigenous medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) drone, the Drishti 10 Starliner, developed by Adani Defence and Aerospace in collaboration with Elbit Systems. With 70% indigenous content, the drone offers 36-hour endurance, a 450 kg payload capacity, and adaptability for surveillance and reconnaissance missions.
INS Surat and INS Nilgiri

Indian Navy got destroyer INS Surat and frigate INS Nilgiri in 2024. These ships, built by the Warship Design Bureau and MDL, enhance India’s naval capabilities, reflecting the focus on Aatmanirbharta. INS Surat, the fourth and final Project 15B destroyer, boasts advanced weapons, AI integration, and speeds over 30 knots.

INS Nilgiri, the first Project 17A frigate, is equipped with cutting-edge missile systems. Both ships have 75% indigenous content.
Testing advanced weapons
In addition to these inductions, India conducted various successful trials and tests of various other lethal advanced weapons this year.
The country test-fired a domestically developed long-range hypersonic missile, capable of carrying payloads over 1,500 km at speeds exceeding Mach 5.

The Navy tested an extended-range Brahmos missile, while the Agni Prime missile, with MIRV technology, also passed its trial.
Defence deals
India signed agreements with several countries to acquire new weapons, including a Rs 28,000 crore deal for MQ-9B Predator drones with the US and the opening of Spain’s C-295 aircraft manufacturing plant in Gujarat’s Vadodara.


The country has also sanctioned various upgrades for its existing arsenal to enhance its battle capabilities.
For example, Sukhoi-30s, which are considered the backbone of IAF, will receive a major makeover to increase their life by 30 more years.

IAF will also soon get its first batch of an upgraded version of its made-in-India LCA Tejas, Tejas MK-1A, which is being developed by HAL.





