The discovery of the fact that the Great Lakes originate from a geological hotspot beneath the ancient supercontinent Pangaea presents a major advancement in the comprehension of the geological history of the Earth. As per the study published in Geophysical Research Letters, surmises that the Cape Verde hotspot, an active hotspot located in the Central Atlantic today, played a major role in defining the Great Lakes region millions of years ago.
How the Cape Verde hotspot shaped the formation of the Great Lakes region?
A hotspot is a plume of molten material rising from the Earth’s mantle, which interacts with the Earth’s crust and can lead to significant geological features, such as volcanoes and large depressions in the Earth’s surface. Hotspots are stationary over time, while the tectonic plates above them move, creating a trail of geological changes. The Cape Verde hotspot is one of such geological features and is located close to the island nation of Cape Verde in the Atlantic Ocean.
Million years ago, Earth was part of the supercontinent Pangaea. During this time, the Cape Verde hotspot lay under what is now the Great Lakes region. With this stretching and weakening, the depression caused by the heated Earth’s crust formed a foundation for what is now the Great Lakes. Such a process, in terms of geology, paved the way for the rest of the region’s developments.
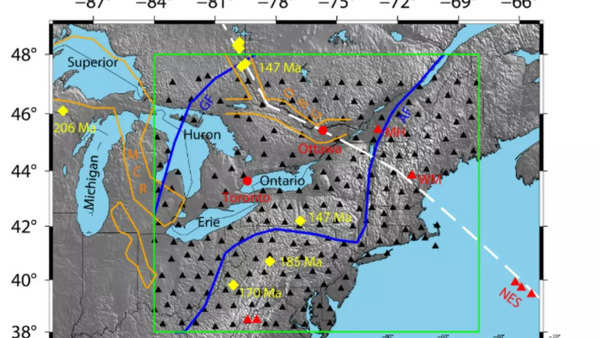
Image source: Advancing Earth and Space Sciences
Role of glaciers in forming the Great Lakes
During the last ice age, glaciers started moving across great parts of North America, and they really helped to mould the landscape further. Scrape the land while moving, erode the depression that was caused by the hotspot, and carve out the more considerable basin they did. The glacial work resulted in creating the large and deep depressions that are now filled with water to create the Great Lakes.
When the ice sheets eventually melted, the meltwater filled the basins with freshwater, and the Great Lakes as we know them today were formed. This happened around 20,000 years ago, after the ice had melted.
Cape Verde hotspot’s impact on the Great Lakes formation
The scientists who led the new research found seismic anomalies in the area of the Great Lakes, known as radial anisotropy. This is a phenomenon whereby seismic waves, which are generated by earthquakes and other seismic activities, travel at different speeds depending on the direction in which they move through the Earth’s crust. Radial anisotropy is often an indication of past deformation of the Earth’s lithosphere, which is the rigid outer layer of the Earth that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle.
These strange seismic patterns indicate that the lithosphere beneath the Great Lakes region was deformed and, possibly by the influence of the Cape Verde hotspot. Through the use of plate reconstruction models, the scientists are able to link these seismic anomalies to the hotspot’s past location beneath the Great Lakes. Such a connection only further solidifies the fact that the hotspot has played a considerable role in the geological formation of the region.
The research revealed that the Cape Verde hotspot lay beneath the Great Lakes region since about 300 million years ago, when North America was part of Pangaea. As the tectonic plates moved, the hotspot moved across what is now the Great Lakes region, traveling beneath areas that would later become Lake Superior, Lake Huron, and Lake Erie. It gradually moved westwards over tens of millions of years, and it eventually was situated under places such as present-day New York and Maryland.
Ongoing research on the influence of hotspots in shaping the Great Lakes and large freshwater basins
The researchers now are looking to continue their study in a more westerly direction with the aim to understand how perhaps the influence of the hotspot extended into other portions of the Great Lakes region. They are further interested in establishing whether there’s a broader trend that connects lake formation to size with regions where once ancient hotspots existed.
This could mean that hotspots are linked to the generation of large lakes, as the geological conditions of hotspots could be the means through which these basins come into existence. If this is the case, then it might open up research avenues into the ways in which hotspots have shaped the Earth’s surface, especially in the context of freshwater lakes.
Connection between the Cape Verde hotspot and the formation of the Great Lakes
The connection between the Cape Verde hotspot and the Great Lakes adds a new layer of understanding to the geological processes that have shaped Earth’s surface over millions of years. By tracing the movements of hotspots beneath ancient supercontinents and studying the resulting seismic anomalies, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of how the Earth’s crust and mantle have interacted to form the landscape we see today.
In addition, the study of ancient hotspots also helps uncover the movements of tectonic plates and the drifting of the continents over the years. It is likely that new insights regarding the geological history of the Earth and its changes will be discovered through further research regarding the role played by hotspots in shaping features on Earth. To this, the Great Lakes’ formation may not be completely attributed to glaciation but has also been connected to ancient volcanism related to the Cape Verde hotspot. These insights thus greatly enhance the perception of the dynamical processes the Earth undergoes in the development and evolution of massive geological features like lakes over scales of geological timescales.
Also Read | Sunita Williams set to perform her first spacewalk in 12 years to last over 6 hours, marking a new milestone in her space career




